Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 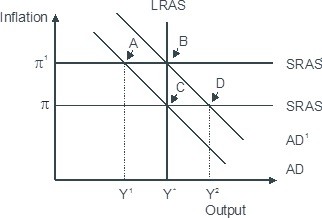
A. D; an expansionary
B. B; no output
C. B; expansionary
D. A; a recessionary
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a war that raises government purchases results in ________ output in the short run and ________ output in the long run.
A. lower; potential B. higher; potential C. higher; higher D. lower; higher
The above figure shows the utility of wealth curve for a homeowner whose only possession is a $50,000 house. If there is a 20 percent chance that the home could be completely destroyed, would this homeowner buy insurance?
A) No, because the homeowner is not risk averse. B) Yes, at any price because the homeowner is risk averse. C) Yes, but only if it costs less than $10,000. D) Yes, but only if it costs less than $20,000.
In comparing the returns on U.S. and German Treasury securities, investors
A) should forecast the future dollar/euro exchange rate. B) may disregard the future dollar/euro exchange rate. C) should assume the future dollar/euro exchange rate is the same as today's. D) should assume the euro will depreciate if the German interest rate is above the U.S. interest rate.
Labor productivity increases when
A) the average number of hours people work goes up. B) the unemployment rate decreases. C) the average output produced per worker during a specified time period increases. D) the average output produced per worker during a specified time period decreases.