In deriving the aggregate demand curve from the aggregate expenditures model, we note that:
A. the real-balances effect is irrelevant to both models.
B. a change in the price level will have no impact on the aggregate expenditures schedule.
C. an increase (decrease) in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule
upward (downward).
D. an increase (decrease) in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule
downward (upward).
D. an increase (decrease) in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule
downward (upward).
You might also like to view...
When the opportunity cost of holding money increases, then
A) the quantity of money supplied increases. B) people want to hold more money. C) the real interest rate falls. D) the nominal interest rate falls. E) people want to hold less money.
Unions first became powerful in the United States in industries dominated by
A) government. B) highly profitable firms. C) large firms. D) small firms.
In an unregulated competitive market, the presence of marginal external cost of a good or service results in overproduction
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
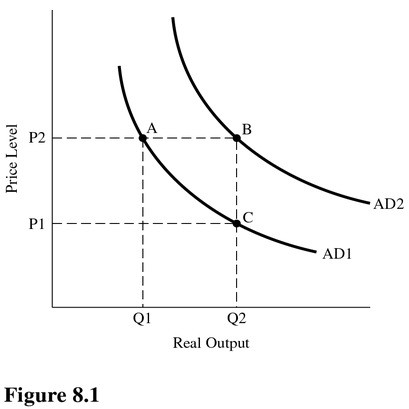 In Figure 8.1, an increase in government spending, ceteris paribus, is best represented as a movement from point
In Figure 8.1, an increase in government spending, ceteris paribus, is best represented as a movement from point
A. A to point C. B. B to point C. C. A to point B. D. C to point A.