Refer to the table below. Given that an individual's opportunity cost of time is $30 per hour, which of the two apartments should she rent?
Apartment Monthly Commuting Time (Hours) Monthly Rent ($)
1 60 3,600
2 20 4,500
The opportunity cost of commuting per month from Apartment 1 = 60 × $30 = $1,800.
Total monthly cost of renting Apartment 1 = $1,800 + $3,600 = $5,400.
The opportunity cost of commuting per month from Apartment 2 = 20 × $30 = $600
Total monthly cost of renting Apartment 2 = $600 + $4,500 = $5,100
Therefore, the individual chooses Apartment 2 as she incurs a lower cost if she rents Apartment 2 than when she rents Apartment 1.
You might also like to view...
From 2007 to 2009 our current account deficit
A. has been cut in half. B. stayed about the same. C. almost doubled. D. more than tripled.
The September 11 attacks had the effect of shifting the
A) IS curve to the right. B) IS curve to the left. C) LM curve to the right. D) LM curve to the left.
Higher interest rates motivate:
A. individuals to spend more on consumption goods. B. individuals to spend more on capital goods. C. firms to invest less in new factories and working capital. D. firms to invest more in new factories and working capital.
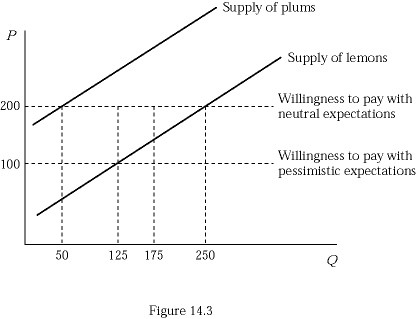 Figure 14.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used refrigerators sold will actually be plums (high quality)?
Figure 14.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used refrigerators sold will actually be plums (high quality)?
A. 50/250 B. 50/300 C. 250/300 D. None of the refrigerators sold will be plums.