A particle moves in the xy plane with a constant acceleration given by 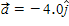 m/s2. At t = 0, its position and velocity are
m/s2. At t = 0, its position and velocity are 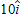 m and
m and ![]()
src="https://sciemce.com/media/2/ppg__cognero__Chapter_4_Two_and_Three_Dimensional_Motion.__media__b88562d4-679d-415b-8c57-03705e7a29d7.PNG" style="vertical-align:middle;" /> m/s, respectively. What is the distance from the origin to the particle at t = 2.0 s?
A. 6.4 m
B. 10 m
C. 8.9 m
D. 2.0 m
E. 6.2 m
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Quintessence is the name of the
a. force that lead to the inflationary period of the universe. b. five dimensional space of the universe. c. force suspected to cause the current acceleration in the rate of expansion of the universe. d. one of the particles of dark matter related to WIMPs. e. the force that holds the proton together.
The Moon has an average density of 3.3 g/cm3. From this number, what can we infer about the composition of the Moon?
A. Its composition is mostly metals and water ice. B. Its composition is entirely silicates. C. Its composition is exactly the same as Earth's. D. Its composition is mostly silicates, with some iron. E. None of these choices are correct.
What is the fundamental reason that Mars, unlike Earth, has become virtually geologically dead?
A) its small size compared to Earth B) its large size compared to Earth C) its farther distance than Earth to the Sun D) its closer distance than Earth to the Sun E) its rapid rotation compared to Earth F) its slow rotation compared to Earth
From Earth, the view of the Milky Way is a thin band of stars across the night sky. The part of the Milky Way galaxy that is described here is the:
A) bulge. B) spiral arm. C) disk. D) halo. E) globular cluster.