The idea of time inconsistency:
A. explains how it can be rational for someone to pay more for something on his credit card than if he were to pay cash for the same thing.
B. explains how it can be rational for someone to say he's going to eat a salad for dinner each night this week and end up eating pizza four out of five nights instead.
C. explains why people refuse to ignore only some sunk costs.
D. Time inconsistency doesn't explain any of these behaviors.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The supply of product X is perfectly inelastic if the price of X increases by ________ and, as a result of the price change, the quantity supplied ________
A. 7%; increases by 5%. B. 10%; stays the same. C. 8%; increases by 8%. D. 5%; increases by 7%.
Use the above figure. Assuming that policy actions are unanticipated, if the economy is at point A and the policy makers want to get to point B, they could
A) decrease taxation. B) increase the money supply. C) increase government spending. D) decrease the money supply.
Refer to Figure 2.1. A movement from point a to point c is most likely caused by:
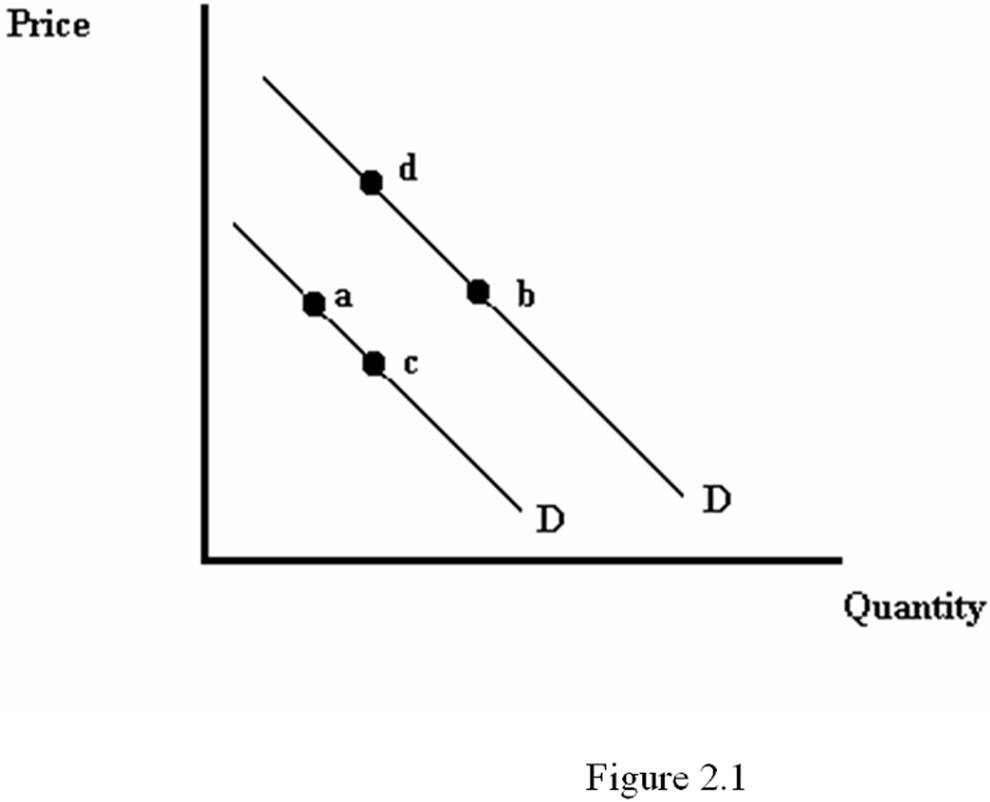
A. a decrease in the price of the good.
B. an increase in consumers' incomes, assuming the good is normal.
C. a decrease in the price of a complementary good.
D. an increase in the price of the good.
Which of the following is not one of the three pillars of productivity growth?
A. Rate of capacity utilization B. Rate of technological improvement C. Rate of improvement in workforce quality D. Rate of capital expansion