What will happen to the U.S. dollar price of a euro and the quantity of euros exchanged when the demand for the euro decreases, but the supply does not change? Has the U.S. dollar appreciated or depreciated?
Please provide the best answer for the statement.
The decrease in the demand for euros decreases the U.S. dollar price of the euro and decreases the equilibrium quantity exchanged for the euro. This change means that the U.S. dollar has appreciated in value because it now requires less U.S. currency to purchase a euro.
You might also like to view...
In 2008, Germany had a budget deficit of 37 billion euros. This deficit resulted in
A) a rightward shift of the supply of loanable funds curve. B) a leftward shift of the demand for loanable funds curve. C) a crowding out effect in which investment decreases. D) the Ricardo-Barro effect and an increase in the interest rate.
A hamburger costs $1.79 in New York and €2.54 in Paris. If the exchange rate is $0.93 per euro, what price difference exists in terms of the European currency?
a. The hamburger sells for €0.13 less in New York. b. The hamburger sells for €0.13 more in New York. c. The hamburger sells for €0.62 less in Paris. d. The hamburger sells for €0.62 more in Paris. e. The hamburger sells for the same price in both cities.
If deficit spending does not contribute to public investment and crowds out private investment, then
A. Future productive capacity will be enhanced. B. The current generation will bear the total burden of the debt. C. The opportunity cost of the debt will be minimized. D. The rate of economic growth will decline, ceteris paribus.
Consider a town with three residents. The residents' demand curves for various acres of a public park are shown below.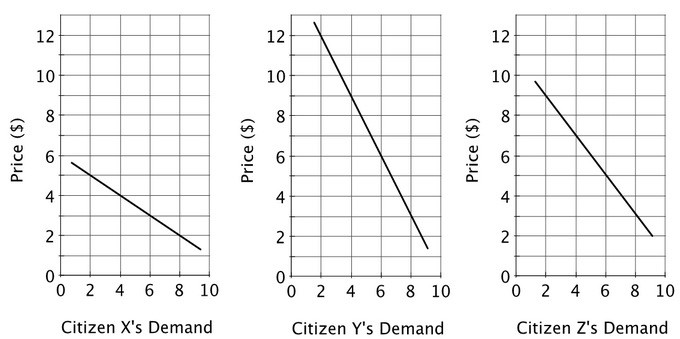 The public is willing to pay $14 for the ________ acre of parkland.
The public is willing to pay $14 for the ________ acre of parkland.
A. $6. B. $8. C. $20. D. $14