A budget constraint illustrates the
a. prices that a consumer chooses to pay for products he consumes.
b. purchases made by consumers.
c. consumption bundles that a consumer can afford.
d. consumption bundles that give a consumer equal satisfaction.
c
You might also like to view...
Consumption spending is $5 million, planned investment spending is $8 million, unplanned investment spending is $2 million, government purchases are $10 million, and net export spending is $2 million. What is GDP?
What will be an ideal response?
A point or product-combination to the left of and inside a budget line:
A. Is attainable, but a combination or point to the right of the line is unattainable B. Is unattainable, but a combination or point to the right of the line is attainable C. Costs more than a combination or point on the budget line D. Costs more than a combination or point outside the budget line
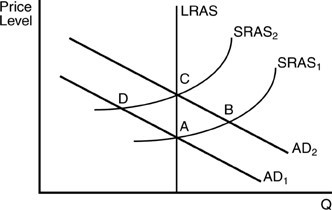 In the above figure, suppose the economy is currently in equilibrium at point C. Applying rational expectations theory, what happens if the Fed announces that it is decreasing the money supply and follows through on its statement?
In the above figure, suppose the economy is currently in equilibrium at point C. Applying rational expectations theory, what happens if the Fed announces that it is decreasing the money supply and follows through on its statement?
A. Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per year will increase. B. The price level will increase. C. The price level will decrease. D. Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per year will decrease.
The interest rate is 4 percent in the U.K. and 3 percent in the U.S. for 90 days. The current spot rate is $2.00/£ and the forward rate is $1.96/£. If a U.S.-based investor expects the spot rate to remain at $2.00/£ in 90 days, the expected uncovered interest rate differential would be ________ in favor of the ________ investment.
A. 2%; dollar B. 2%; pound C. 1%; pound D. 1%; dollar