The gross domestic product for the above economy is:

A. $100.
B. $95.
C. $110.
D. $107.
C. $110.
You might also like to view...
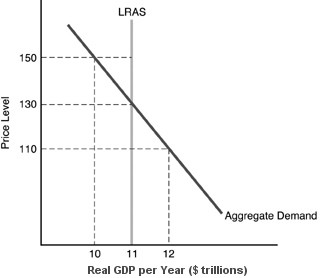 In the above figure, if the price level is 110
In the above figure, if the price level is 110
A. total expenditures exceed total planned expenditures. B. total planned production equals total expenditures. C. total planned production exceeds total expenditures. D. total planned production is less than total expenditures.
Monopolistic competition and perfect competition are different in that
A. only monopolistically competitive firms advertise. B. only perfectly competitive firms maximize profits where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. C. only perfectly competitive firms are characterized by long-run economic profits of zero. D. only monopolistically competitive firms can earn economic losses in the short-run.
If the demand for a life-saving drug was perfectly inelastic and the price doubled, the quantity demanded would
A) also double. B) decrease by 50%. C) be cut in half. D) remain constant.
Which is not true of price discrimination?
A. Successful price discrimination implies that the producer can separate customers into easily identifiable groups. B. Successful price discrimination will provide the firm with more profit than if it does not discriminate. C. Successful price discrimination will generally result in a lower level of output than would be the case under a single-price monopoly. D. It exists when price differences depend critically on different buyers' evaluations of a product.