In the description of labor costs associated with fishing, the textbook measures the cost of labor that corresponds with different quantities of fish. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Labor costs for fish production cannot be estimated.
b. The cost of labor increases at an increasing rate at low levels of output.
c. Labor costs increase at the same rate over all ranges of output.
d. At higher levels of output, the cost of labor increases at an increasing rate.
e. At higher levels of output, the cost of labor decreases at an increasing rate.
D
You might also like to view...
In theory the market's willingness-to-pay (WTP) should be equal to the market's willingness-to-accept (WTA). In other words, if you are willing-to-pay $1 for an incremental improvement in tap water quality, then you should be willing-to-accept $1 for an incremental decrease in tap water quality. In practice, however, the two are often estimated to be unequal. Which of the following helps to explain this disparity?
a. the WTA/WTP disparity b. the endowment effect c. benefit transfer d. value of statistical life e. cost-benefit analysis f. expected value g. risk and uncertainty h. None of the above.
What are some of the possible ways in which we could reduce the natural rate of unemployment?
What will be an ideal response?
Credence goods are particularly susceptible to the lemons problem because
A) they have qualities that are difficult for producers to fully assess. B) they have qualities that are difficult for consumers to fully assess. C) creative responses among producers create volatility in market supply. D) creative responses among consumers create volatility in market demand.
In Figure 1.2, which labeled points represent the existence of unemployment? 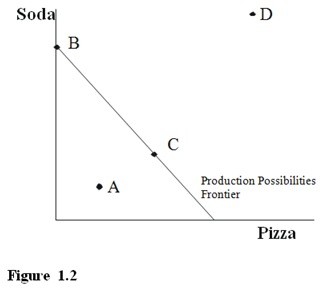
A. only A B. only B and C C. only D D. A, B, and C