A set of indifference curves on a graph is called
A. a budget map.
B. a cluster.
C. an indifference map.
D. a difference map.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Bananas and apples are substitutes. When the price of bananas rises, and a technological advance in apple production occurs at the same time
A) the equilibrium price of apples rises and the equilibrium quantity of apples falls. B) the equilibrium price of apples rises and the equilibrium quantity of apples might rise or fall. C) the equilibrium quantity of apples rises and the equilibrium price of apples might rise or fall. D) the equilibrium price of apples rises and the equilibrium quantity of apples rises.
Which of the following is not one of the strengths of the Cobb-Douglas production function?
A) Both marginal product and returns to scale can be estimated from it. B) It can be converted into a linear function for ease of calculation. C) It shows a production function passing through increasing returns to constant returns and then to decreasing returns. D) The sum of the exponents indicates whether returns to scale are increasing, constant or decreasing.
Suppose a tax on buyers has been imposed in the graph shown. Once the tax is in place, the buyers purchase ____ units and pay ____ for each one.
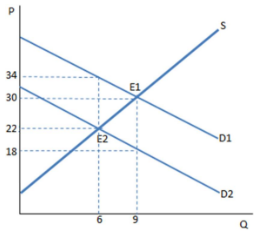
A. 6; $22
B. 6; $34
C. 9; $18
D. 9; $30
Which of the following statements best describes a comparison between Keynesian and neoclassical models?
a. Neoclassical economics tends to view deflation as a price that might sometimes be paid for lower unemployment; Keynesian economics tends to view deflation as a cost that offers no offsetting gains in terms of lower unemployment. b. Keynesian economics tends to view deflation as a price that might sometimes be paid for lower unemployment; neoclassical economics tends to view deflation as a cost that offers no offsetting gains in terms of lower unemployment. c. Neoclassical economics tends to view inflation as a price that might sometimes be paid for lower unemployment; Keynesian economics tends to view inflation as a cost that offers no offsetting gains in terms of lower unemployment. d. Keynesian economics tends to view inflation as a price that might sometimes be paid for lower unemployment; neoclassical economics tends to view inflation as a cost that offers no offsetting gains in terms of lower unemployment.