Suppose the income elasticity of demand for a private college education is equal to 1.5 . This means that
a. every $1 increase in income provides an incentive for a $1.50 increase in expenditures on private college education
b. every $1.50 increase in income provides an incentive for a $1 increase in expenditures on private college education
c. a 10 percent increase in income causes a 15 percent increase in the demand for a private college education
d. a 15 percent increase in income causes a 10 percent increase in the demand for a private college education
e. a 10 percent decrease in private college tuition will have a large enough income effect to increase spending on private college education by 15 percent
C
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph for a perfectly competitive firm generating a loss in the short run to answer the next question.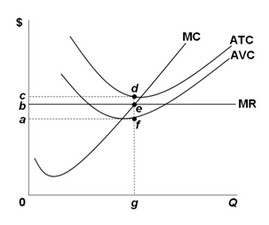 Which area in the graph represents the loss generated by the firm?
Which area in the graph represents the loss generated by the firm?
A. bcde B. 0beg C. abef D. acdf
Assume there is a simultaneous decrease in the incomes of people in the market for new homes and a decrease in the wages paid to carpenters, plumbers, and electricians
All else constant, we can predict, with certainty, that in the market for new homes the equilibrium: A) quantity of new homes will decrease. B) quantity of new homes will increase. C) price of new homes will decrease. D) price of new homes will increase.
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large tax cut will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; higher; higher B. expansionary; higher; potential C. recessionary; higher; potential D. recessionary; lower; lower
If net investment is zero, then
A. gross investment is less than depreciation. B. depreciation is zero. C. gross investment is greater than depreciation. D. gross investment equals depreciation.