If it took as many dollars to buy goods in the United States as it did to buy enough currency to buy the same goods in India, the real exchange rate would be computed as how many Indian goods per U.S. goods?
a. one
b. the number of dollars needed to buy U.S. goods divided by the number of rupees needed to buy Indian goods
c. the number of rupees needed to buy Indian goods divided by the number of dollars needed to buy U.S. goods
d. None of the above is correct.
a
You might also like to view...
Patent trolls ________
A) are paid by innovative firms to the federal government B) buy up patents then attempt to extract large payments from firms using similar technology C) develop new machines and machine processes in small-scale firms, rather than large corporations D) can evolve into natural monopolies
To obtain an estimator that reproduces the fixed effects estimates on the time-varying explanatory variables, _____.
A. ?one must check whether the time-demeaning allows one to interpret the estimates B. ?one must check whether time-constant variables can be included in the fixed effects C. ?one must be able to interpret the time variations D. ?one must be careful in constructing the time averages
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the short run would be: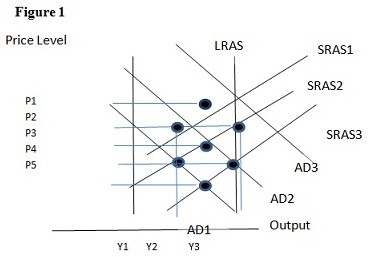
A. P1 and Y2. B. P3 and Y1. C. P2 and Y2. D. P2 and Y3.
(Last Word) The Great Recession of 2007-2009 significantly increased:
A. both the rate of unemployment and the average length of time people were unemployed. B. the rate of unemployment but not the average length of time people were unemployed. C. the average length of time people were unemployed but not the rate. D. both the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment.