In a lead-shot tower, spherical 0.95-cm-diameter BB shots are formed by drops of molten lead which solidify as they descend in cooler air. At the terminal velocity, i.e., when the drag equals the gravitational force, estimate the total heat transfer coefficient if the lead surface is at 171°C, the surface of the lead has an emissivity of 0.63, and the air temperature is 16°C. Assume CD = 0.75 for the first trial calculation.
GIVEN
• Spherical lead-shot falling through the air at terminal velocity
• Shot diameter (D) = 0.95 cm = 0.0095 m
• Lead surface temperature (Ts) = 171°C = 494 K
• Lead surface emissivity (?) = 0.63
• Air temperature (T?) = 16°C 289 K
• Assume CD = 0.75 for the first trial calculation FIND
• The total average heat transfer coefficient (htotal). ASSUMPTIONS
• The surroundings act as a black body enclosure at T?
SKETCH
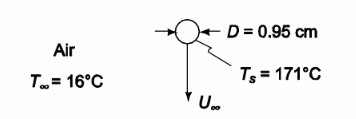
The weight of the lead shot is
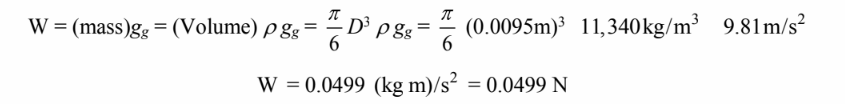
Terminal velocity occurs when the weight is balanced by the drag force which is given
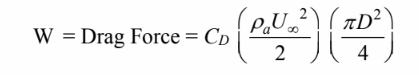
Solving for the terminal velocity
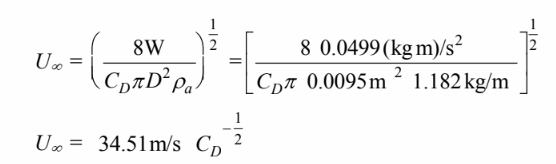
Using the recommended drag coefficient for the first iteration
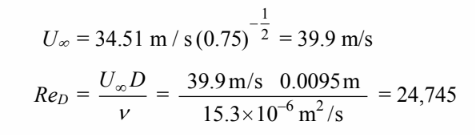
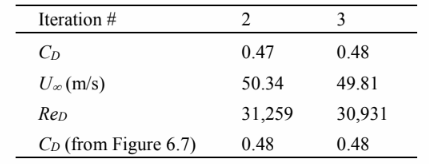
Repeating this procedure for further iterations
The Nusselt number is given by
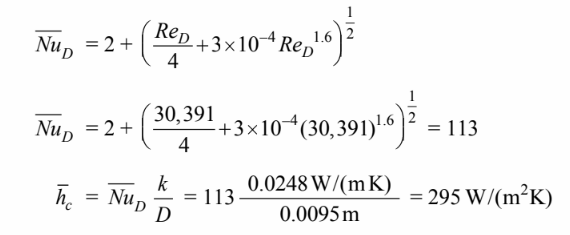
The total rate of heat transfer can be used to calculate the total heat transfer coefficient as follows
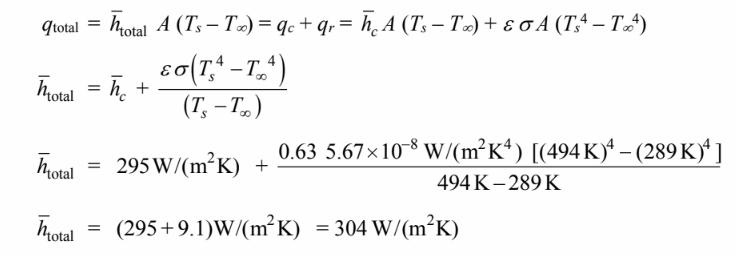
COMMENTS
97% of the heat transfer is due to convection.
You might also like to view...
When an object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, the image is 3.0 cm in front of the mirror? What is the focal length of the mirror?
A) -0.25 cm B) 15 cm C) 4.0 cm D) 2.4 cm E) -1.3 cm
During a nuclear reaction, the particles involved lose 4.8 × 10-28 kg of mass. How many joules of energy are released by this reaction? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s)
A) 1.4 × 10-19 J B) 5.3 × 10-45 J C) 2.1 × 10-40 J D) 4.3 × 10-11 J E) 1.6 × 10-36 J
A proton in a certain particle accelerator has a kinetic energy that is equal to its rest energy
What is the TOTAL energy of the proton as measured by a physicist working with the accelerator? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, mproton = 1.67 × 10-27 kg) A) 1.50 × 10-10 J B) 8.77 × 10-10 J C) 3.01 × 10-10 J D) 2.07 × 10-10 J E) 5.69 × 10-11 J
Two objects having masses m1 and m2 are connected to each other as shown in the figure and are released from rest
There is no friction on the table surface or in the pulley. The masses of the pulley and the string connecting the objects are completely negligible. What must be true about the tension T in the string just after the objects are released? A) T = m2g B) T > m2g C) T < m2g D) T = m1g E) T > m1g