When higher prices result in a lower quantity demanded, economists call this relationship:
A. The demand curve
B. Price and demand model
C. The law of demand
Ans: C. The law of demand
You might also like to view...
Use the information below to explain adjustments that move the economy to a long-run equilibrium. Assume that firms and workers have adaptive expectations
The current unemployment rate = 7%. The natural rate of unemployment = 5.5%. Last year's inflation rate = 5%. This year's inflation rate = 4%.
The supply curve of labor to industry in the Lewis model is horizontal if there is surplus labor in agriculture. This condition persists as long as
a. the marginal product of labor is less than the average product of labor in agriculture. b. the marginal product of labor in agriculture is less than the marginal product of labor in industry. c. there are diminishing returns to labor in agriculture. d. the marginal product of labor in agriculture is zero.
When quantity demanded decreases at every possible price, the demand curve has
a. shifted to the left. b. shifted to the right. c. not shifted; rather, we have moved along the demand curve to a new point on the same curve. d. not shifted; rather, the demand curve has become flatter.
Figure 6-1
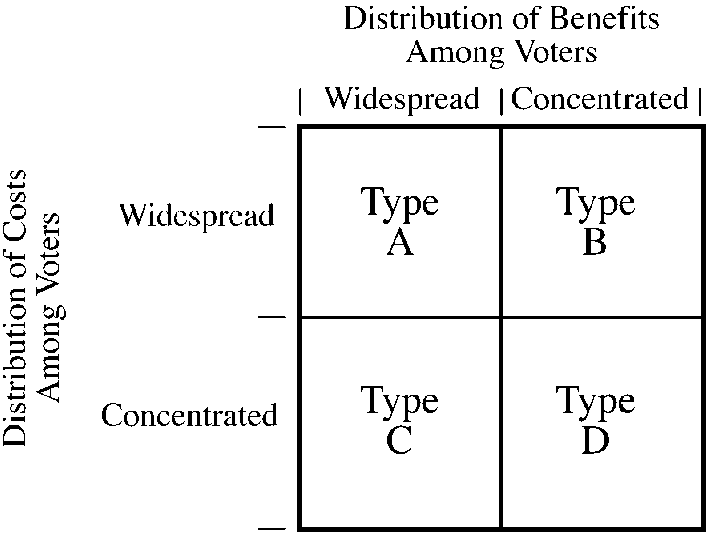
illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. Programs that give subsidies to a small group of producers at general taxpayer expense would be considered
a.
type A projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
b.
type B projects, and the government would be likely to undertake many of these projects even when they were counterproductive (inefficient).
c.
type C projects, and the government would be likely to fail to undertake many of these projects even when they were productive (efficient).
d.
type D projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.