Because many emerging market countries have not developed the political or monetary institutions that allow the successful use of discretionary monetary policy
A) they have little to gain from pegging their exchange rate to an anchor country like the U.S. or Germany.
B) they have little to gain from using a nominal anchor, because it would mean a monetary policy that is overly expansionary.
C) they have very little to gain from an independent monetary policy, but a lot to lose.
D) they would be better off giving their central bankers the independence to use discretion, rather than take their discretion away through any nominal anchor.
C
You might also like to view...
Union membership declined during the 1920s due to:
a. failure of a number of strikes. b. increase in real wages left the labor force satisfied. c. firms' use of "yellow-dog" contracts. d. poor union leadership. e. All of the above.
Which of the following situations resulted from the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)?
a. The cost of tortillas in Mexico decreased. b. Corn export to the U.S. from Mexico declined. c. Corn export to the U.S. from Mexico increased. d. The cost of tortillas in the U.S. increased.
Requiring a firm with international operations to follow the standards of its home country instead of those of the foreign country has all of the following advantages EXCEPT
A) it takes care of the fear of a race-to-the-bottom by making it impossible for a home-based company to exploit low standards.
B) it shifts the costs of improved standards to firms and consumers in high-income countries.
C) it removes the threat of domestic firms relocating abroad for low standards and ensures that any relocation that takes place is due to foreign comparative advantage.
D) it avoids the problems of high-income countries dictating what standards are to be used. In this situation, firms that cross national boundaries must conform to whichever standards are higher.
E) it is a comprehensive measure, since it addresses the problem of production in foreign firms as well as firms from high-standards countries that relocate abroad.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be: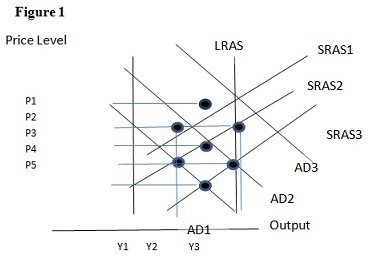
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y3. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y2.