What is meant by direct regulation of pollution emissions? What is the problem with this method of pollution control?
What will be an ideal response?
Direct regulation typically takes the form of uniform treatment of polluters. Direct regulations can include requiring all polluters to reduce pollution by a fixed amount or install similar pollution abatement equipment. Unlike market-based solutions to pollution control, direct regulation does not take into account differences in firms' costs of reducing pollution.As a result, the cost to society of pollution abatement may be larger than it needs to be.
A-head: ECONOMICS OF THE ENVIRONMENT
Concept: Direct regulation
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 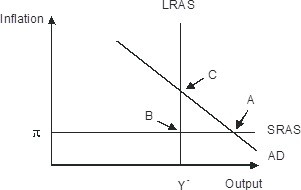
A. Rising; B; C B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; A; B D. Rising; A; C
A natural experiment is an empirical study:
A) in which the predictions of the model are not required to be tested with data. B) in which some process, outside the control of the experimenter, has assigned subjects to control and treatment groups in a random or nearly random way. C) in which the researcher assigns subjects to control and treatment groups to verify a cause-effect relationshi
The table above presents the production possibilities frontier for a nation
Using the information in the table, when moving from possibility C to D, the cost of 1 unit of a capital good in terms of the consumption goods forgone is ________ consumption goods per capital good. A) 10 B) 25 C) 15 D) 20 E) an undefined amount of
The putting up of outside collateral is
A) one form of the moral hazard problem. B) one form of the adverse selection problem. C) a signal of a high-quality borrower. D) a signal of a low-quality borrower.