The efficient level of recycling equates the
A) marginal cost of scrap disposal to the marginal benefit from not using virgin materials.
B) marginal cost of recycling to the marginal benefit from not using virgin materials.
C) marginal cost of scrap disposal to the marginal cost of recycling.
D) marginal private cost of disposal to the marginal cost of recycling.
E) per-unit refund from recycled materials to the marginal benefit from not using virgin materials.
C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following accurately measures the welfare or happiness of society?
A) Nominal GDP B) Real GDP C) Both Nominal GDP and Real GDP D) None of the above.
When a negative externality is present in a market, when a quota is imposed, it is:
A. efficient, because the market consumes the efficient level. B. not efficient, because individuals' net benefits from the amount set by the quota are different. C. efficient, because the net benefit of everyone at the amount set by the quota is equal. D. not efficient, because the marginal cost outweighs the marginal benefit for too many consumers at the amount set by the quota.
Assume that the central bank lowers the discount to increase the nation's monetary base. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and real GDP in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic system returns to complete equilibrium
a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls and real GDP falls. b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises and real GDP rises. c. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises and real GDP remains the same. d. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period and real GDP remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
A nation can produce two products: tanks and autos. The table below is the nation's production possibilities:
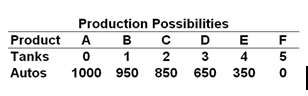
Refer to the above table. If the nation produces more and more tanks, the opportunity cost of each additional tank in terms of autos:
A. Remains constant
B. Falls
C. Increases
D. Cannot be measured