In the long run for a competitive firm,
A. the firm is making economic profits.
B. the firm is at the bottom of its short run average cost curve.
C. the marginal cost is greater price.
D. the firm is at the top of its long run average cost curve.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The demand for a product is inelastic whenever
A. the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price. B. the percentage change in quantity demanded is higher than the percentage changes in price. C. the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage changes in price. D. the quantity demanded changes by zero when price changes.
The act of buyers and sellers freely conducting business in a market
a. voluntary exchange b. free market system c. profit motive d. fraud
Referring to a production possibilities curve and the goods being compared, depict the economic event. Widespread use of the assembly line revolutionizes U.S. industry in the early 20th century (capital vs. consumer goods).
A. A movement from a point inside the curve to a point on the curve B. A movement from a point on the curve to a point inside the curve C. A shift in the entire curve to the right (outward) D. A shift in the entire curve to the left (inward)
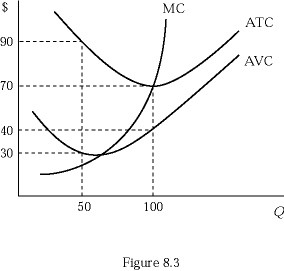 Figure 8.3 shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost curves. At Q = 50, the average fixed cost is:
Figure 8.3 shows a firm's marginal cost, average total cost, and average variable cost curves. At Q = 50, the average fixed cost is:
A. $30. B. $40. C. $50. D. $60.