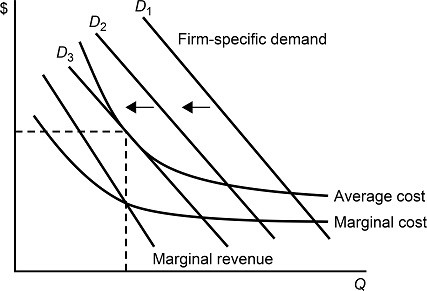
 Figure 8.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3, in the long run we would expect:
Figure 8.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3, in the long run we would expect:
A. the firm to earn a zero economic profit.
B. the firm to charge a price equal to its marginal cost.
C. the firm to increase its output level.
D. the firm to produce at the lowest average cost.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements correctly highlights a difference between real GDP and nominal GDP?
A) Real GDP includes the value of goods and services produced by foreign firms, while nominal GDP does not. B) Real GDP strips out the effect of changing prices on the value of goods and services produced, while nominal GDP does not. C) Real GDP includes the value of goods and services produced by domestic firms in foreign countries, while nominal GDP does not. D) Real GDP does not take into account the value of goods produced and also services provided, while nominal GDP takes these into account.
The level of output produced when the labor market is in equilibrium is called
A) global production output. B) natural output. C) product market equilibrium output. D) potential output.
The Smoot-Hawley Act introduced
A) opportunities for expanding U.S. foreign trade. B) the highest tariffs set by the United States in the last 90 years. C) a framework promoting international free trade. D) revenue tariffs as a major source of U.S. government revenues.
Suppose a fast food restaurant was one of many hiring workers, the minimum wage was $7.25 an hour, and it was paying $7.25 an hour to new employees. Suppose a worker earns a $0.75 raise to $8.00 an hour. Now suppose the minimum wage rises to $8.25 and hour. This worker would be paid
A. $8.00 an hour. B. $9.00 an hour. C. $8.25 an hour. D. somewhere between $8.25 and $9.00 an hour depending on the policies of the restaurant.