Mass on a Spring: A 2.0 kg box is traveling at 5.0 m/s on a smooth horizontal surface when it collides with and sticks to a stationary 6.0 kg box. The larger box is attached to an ideal spring of force constant (spring constant) 150 N/m, as shown in the figure. Find (a) the amplitude of the resulting oscillations of this system, (b) the frequency of the oscillations and (c) the period of the oscillations.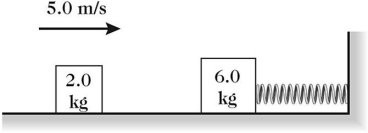
What will be an ideal response?
(a) 0.29 m, (b) 0.69 Hz, (c) 1.5 s
You might also like to view...
The Zeeman effect can be used to determine the _______ our Sun and other stars
a. rotation speed of b. mass of c. color of d. magnetic field on e. radial velocity toward or away from
The deflection of air and ocean currents from their original direction of motion due to the rotation of Earth is called ________.
A. differentiation B. precession C. revolution D. the Coriolis effect E. circulation
The resultant of a 40-N force at right angles to a 30-N force is
A) 30 N. B) 40 N. C) 50 N. D) greater than 50 N.
If Schroedinger's equation is applied to the double-slit experiment with electrons, it enables us to predict
A) the exact motion of each electron. B) the slit through which each electron passes. C) the distribution of electric charge within each electron. D) the probability pattern for electron impacts. E) the electromagnetic wave for each electron.