What effects does solar activity have on Earth?
What will be an ideal response?
Evidence suggests that there is a link between solar activity and the amount of solar energy Earth receives. Solar activity can affect Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere. Solar flares release energy as short-wavelength photons plus high-energy protons and electrons. X-ray and UV photons reach Earth and increase ionization in our upper atmosphere, which can interfere with radio communications. Particles from flares reach Earth as gusts in the solar wind, which can distort Earth's magnetic field and disrupt navigation systems. Solar flares can also cause surges in electrical power lines and damage Earth satellites. The solar wind interacts with Earth's magnetic field and create aurorae.
You might also like to view...
For experiments involving the setup shown in figure Q4.1b, which of the following possible results (if seen) regarding the final value displayed by the voltmeter would probably not be consistent with the wave model of light? 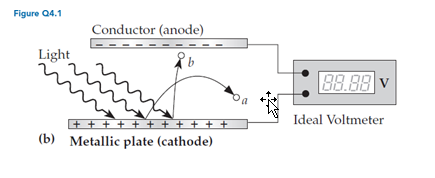
A. It increases as the light’s intensity increases. B. It is independent of the light’s intensity. C. It varies as the light’s wavelength changes. D. It increases as the rate of electron ejection increases.
Ten parsecs is about
A) 150 million kilometers. B) 10,000 seconds. C) 10 parallax seconds of angle. D) 32.6 light-years.
A charged particle (mass = m, charge = q > 0) moves in a region of space where the magnetic field has a constant magnitude of B and a downward direction. What is the magnetic force on the particle at an instant when it is moving horizontally toward the north with speed v?
a. qvB toward the east b. Zero c. qvB toward the west d. qvB upward e. qvB toward the south
A generator produces 60 A of current at 120 V. The voltage is usually stepped up to 4500 V by a transformer and transmitted through a power line of total resistance 1.0 ?
Find the percentage power lost in the transmission line if the voltage is not stepped up. A) 0.018% B) 0.036% C) 5.0% D) 25% E) 50%