Define producer surplus. Using a graph, illustrate producer surplus for a firm with an avoidable fixed cost. Why is it convenient to focus on producer surplus when analyzing policy changes?
What will be an ideal response?
A firm's producer surplus equals its revenue less its avoidable costs, which includes both its variable cost and its avoidable fixed costs, but does not include its sunk costs. Producer surplus for output level Q is illustrated in Figure 9.8.
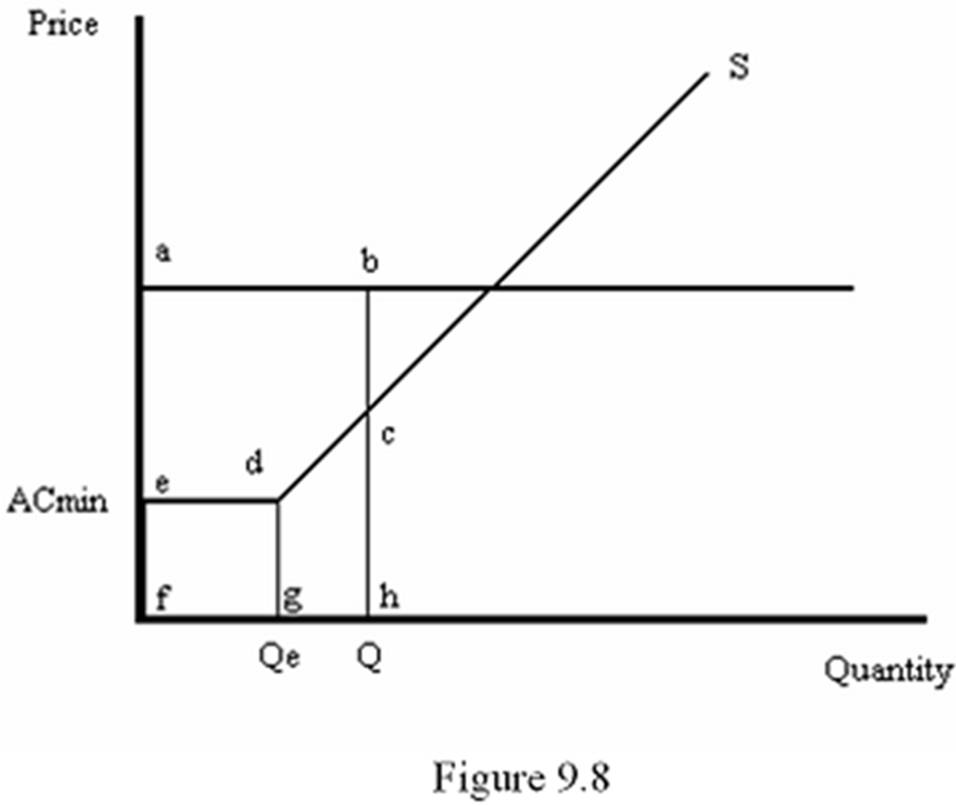
Producer surplus is measured by the area abhf (which represents revenue) minus area chgfed (which represents avoidable costs). Producer surplus is convenient to use because it is easily measured using a supply curve.
You might also like to view...
Purchasing power parity's assumption that the real exchange is constant
A) is correct in nearly all instances. B) would be correct were it not for the existence of trade barriers. C) is not reasonable. D) is correct for trade between the United States and Japan, but incorrect in most other bilateral trading relations.
Which of the following represents the law of supply?
A) An increase in the price of a good causes an increase in the supply of that good. B) An increase in the price of a good causes a rightward shift of the supply curve for that good. C) An increase in the price of a good causes an increase in the quantity supplied of that good. D) all of the above
What is the end result when each prisoner follows his dominant strategy?

a. Each prisoner serves one year in prison.
b. Each prisoner goes free.
c. Each prisoner serves ten years in prison.
d. Each prisoner serves six years in prison.
Which of the following is an example of a seller?
a. Abrams, Kent, and Wallace, Ltd. provide legal services. b. Charles obtains a part for his automobile. c. Optics, Inc. updates their lens-making equipment. d. Solar, Ltd. hires a top salesperson for its new line of products.