Farmer Fanny sells her crops in a perfectly competitive market. If she produces 500 bushels for total revenue of $3,000 and if harvesting the 501st bushel would raise her total cost from $2,500 to $2,510, her
a. revenue will increase by $4 if she harvests the 501st bushel
b. revenue will fall by $4 if she harvests the 501st bushel
c. average fixed cost will rise if she harvests the 501st bushel
d. profit will fall by $10 if she harvests the 501st bushel
e. profit will fall by $4 if she harvests the 501st bushel
E
You might also like to view...
To reduce the chance of investigations and orders to cease production, businesses should
A. adhere to government regulations. B. specialize. C. purchase the most up-to-date technology available. D. lobby members of Congress.
Refer to the graphs shown, which depict a perfectly competitive market and firm. If market demand is D0: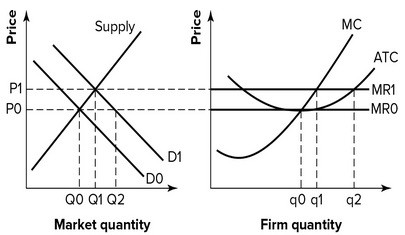
A. the firm will raise the price above P0 to increase profit. B. this market is in short-run equilibrium but not long-run equilibrium. C. this market is in long-run equilibrium because the firm is earning zero economic profit. D. this market is in long-run equilibrium because the firm is earning positive economic profit.
Suppose an economist collects the following data between May and December of a given year: gasoline prices rose sharply, consumer incomes remained constant, consumers purchased more fuel efficient vehicles than in the previous year, the size of the population did not change, sales of gasoline decreased by 15 percent. Which of the following theories could be tested with this information?
A. When the price of gasoline rises, gasoline purchases fall. B. When consumer incomes rise, gasoline purchases rise. C. When the population increases, purchases of fuel efficient vehicles increase. D. No economic theory could be tested with this information.
What does the phrase "internalizing an external cost" mean?
A) limiting the extent to which domestic firms can outsource production B) prohibiting economic activities that create externalities C) forcing producers to factor into their production costs the cost of the externalities created in the production of their output D) finding a way to address cross-border pollution