Consider the following:
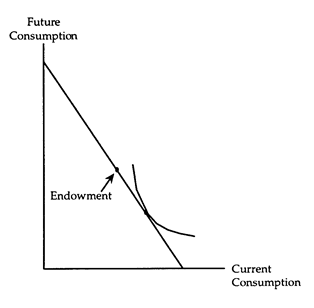
(i) The accompanying diagram shows a net borrower. Complete the diagram to show how a net borrower is affected by a rise in the interest rate. Is the net borrower better off or worse off? Does the net amount borrowed increase or decrease? Explain, using substitution and income effects.
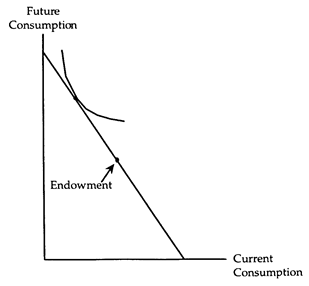
(ii) The accompanying diagram shows a net lender. Complete the diagram to show how a net lender is affected by a rise in the interest rate. Is the net lender better off or worse off? Does the net amount lent increase or decrease? Explain, using substitution and income effects.
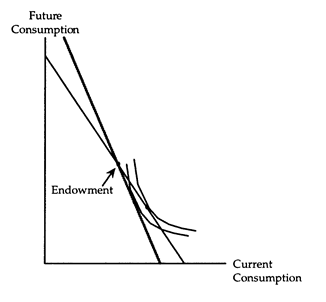
(i) A rise in the interest rate makes a net borrower worse off. Both the substitution and income effects cause a net borrower to reduce his current consumption, so the net amount borrowed must fall. These results are verified in the accompanying diagram.
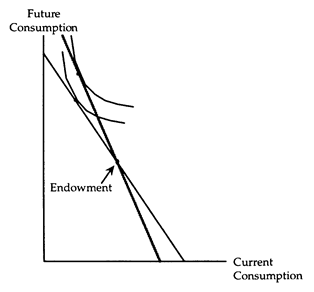
(ii) A rise in the interest rate makes a net lender better off. The substitution effect causes a net lender to reduce his current consumption, but the income effect causes him to increase his current consumption. Thus, current consumption-and hence the net amount lent-may either rise or fall. These results are verified in the accompanying diagram.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 4-3. If the market price is $3.00, what is the consumer surplus on the second ice cream cone?
A) $0 B) $0.50 C) $3.00 D) $5.50
A. What is the difference between a horizontal merger and a vertical merger?
b. Give an example of each type of merger. c. Could a horizontal merger be welfare improving? What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following acts prohibits directors of one company from sitting on the board of a competitor?
a. Sherman Act b. Federal Trade Commission Act c. Robinson-Patman Act d. Clayton Act
Which of the following is a possible regulation strategy for a natural monopoly? a. Requiring the monopolist to set a price equal to the average cost of a good b. Imposing a tariff on the import of a monopolist's good
c. Taxing the income of the monopolist d. Imposing a price floor on a monopolist's good