In a world with few impediments to capital mobility, the domestic interest rate equals the sum of the foreign interest rate and the expected depreciation of the domestic currency, a situation known as the
A) interest parity condition.
B) purchasing power parity condition.
C) exchange rate parity condition.
D) foreign asset parity condition.
A
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the next question.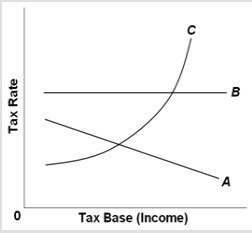 The relationship between the average tax rate and the tax base in a proportional tax would be represented by
The relationship between the average tax rate and the tax base in a proportional tax would be represented by
A. curve A. B. curve B. C. curve C. D. none of the curves.
Refer to Figure 11-4. The movement from E to B to D in the figure above illustrates
A) diminishing returns to capital. B) an improvement in technology. C) diminishing returns to labor. D) a decline in capital per worker.
If a comparative advantage implies that a country can produce a product at a lower opportunity cost than another country then why do we see two countries often trading the same goods? For instance, for most agricultural products the U.S
has a comparative advantage. Japan, one of America's largest trading partners has a comparative advantage in the production of most economy cars. Explain what is going on here when we still see the U.S. exporting cars to Japan and the U.S. importing some foods from Japan.
According to the graph shown, the equilibrium price is ______ and equilibrium quantity is ____.

According to the graph shown, the equilibrium price is ______ and equilibrium quantity is ____.
A. $5; 30
B. $10; 20
C. $20; 10
D. $15; 30