Discuss the second welfare theorem. How can societies use competitive markets to achieve both efficiency and equity?
What will be an ideal response?
The second welfare theorem tells us that every Pareto efficient allocation is a competitive equilibrium for some initial allocation of resources and it suggests that, in principle, societies can use competitive markets to achieve both efficiency and equity. If a competitive outcome is inequitable, the problem is with the initial distribution of resources, not the market institution. If society can redistribute those resources in an equitable manner, competitive markets will deliver the most equitable Pareto efficient allocation. Such redistributions include lump-sum transfers.
You might also like to view...
Import duties ranging from 28 percent to 113 percent on Chinese frozen and canned shrimp are an example of a policy that:
A. protects domestic producers from foreign producers. B. uses regulations and taxes to protect domestic consumers. C. protects domestic fisheries from overfishing. D. protects domestic consumers from foreign producers.
The intersection of the aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve occurs at the economy's equilibrium level of
A) real investment and interest rate B) real disposable income and unemployment C) real national output and the price level D) government expenditures and taxes E) imports and exports
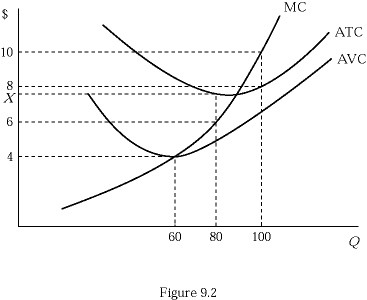 Figure 9.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose that market price falls to $6. If the firm produces at an output level that causes it to suffer an economic loss of $120, its average total cost (X) is:
Figure 9.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose that market price falls to $6. If the firm produces at an output level that causes it to suffer an economic loss of $120, its average total cost (X) is:
A. $8. B. $7.50. C. $6.50. D. $4.
New growth theory is concerned with
A. finding a good way to measure economic growth. B. understanding how compounding works. C. increasing the savings rate in the U.S. D. understanding the forces that increase productivity.