Relative to a stationary observer, a moving clock
A) always runs slower than normal.
B) always runs faster than normal.
C) keeps its normal time.
D) can do any of the above. It depends on the relative velocity between the observer and the clock.
E) can do any of the above. It depends on the relative energy between the observer and the clock.
A
You might also like to view...
To be dimensionally consistent, distance [L], acceleration 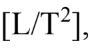 and time [T] must be related as follows.
and time [T] must be related as follows.
A. 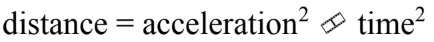
B. 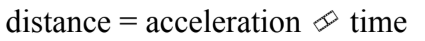
C. 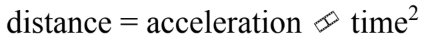
D. 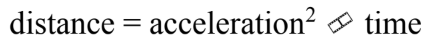
In the time between two closest approaches to Earth, Venus rotates almost exactly five times relative to the Sun. The consequence of this is that:
A) Earth always presents the same face to Venus at inferior conjunction. B) Venus always presents the same face to Earth at inferior conjunction. C) Venus presents the opposite hemisphere to Earth at each inferior conjunction. D) Venus presents the opposite hemisphere to Earth at each superior conjunction. E) Venus' rotation is completely unrelated to the distant Earth.
How much electrical charge is needed to raise an isolated metal sphere of radius 1.0 m to a potential of 1.0 × 10^6 V?
The width of a nuclear state is found to be 10-2 eV. The corresponding lifetime of this state is
A) 10-36 s. B) 10-2 s. C) 10-4 s. D) 4 × 10-13 s. E) 7 × 10-14 s.