Based on the demand curves for perfectly competitive firms and monopolists, the loss in revenue due to price effect applies to ______.
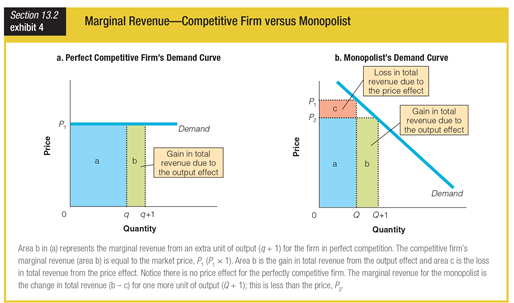
a. only monopolists
b. only perfectly competitive firms
c. both monopolists and perfectly competitive firms
d. neither monopolists nor perfectly competitive firms
a. only monopolists
You might also like to view...
Refer to Scenario 11.1. How much would Mariana expect to pay each landowner for his or her land?
A) $200,000 B) $400,000 C) $600,000 D) $3 million
Jane is deciding whether to go to school for 8 weeks this summer. The cost of tuition and textbooks is $1,700 and housing and other expenses will cost her $600
If she does not go to school, she will live in her parents' house for free and they will cover her food and other expenses for her. Also, if Jane does not go to summer school she could work fulltime. But the best job she can get pays only $600 per week, and Jane would only agree to give up her free time for no less than $750 per week. However, if she goes to summer school, she'll have to spend 40 hours a week attending classes and studying. a) What will the summer school cost Jane in terms of money spent? b) What are the opportunity costs of going to summer school that Jane does not pay explicitly? Explain. c) What is Jane's total opportunity cost of going to school this summer? Explain your answer. d) Suppose that if Jane does not go to summer school, she will eventually take the classes anyway. What is Jane's marginal benefit of going to summer school? e) Suppose Jane decides to go to school in the summer. Explain her decision using the concepts of marginal cost and marginal benefit.
When the United States engaged in quantitative easing from 2008 to 2014, why didn't the money supply rise sharply?
A) Foreigners wanted all the new dollars created by the Federal Reserve. B) Banks held the increased monetary base as excess reserves. C) The Fed offset the increased monetary base by raising reserve requirements. D) The Fed offset the increased monetary base by buying foreign currency.
Recessionary gaps are most likely to be accompanied by
A. inflation. B. inventory reductions. C. unemployment. D. expanding output.