To understand why someone cannot get a job, it helps to know the three types of unemployment. List the three types of unemployment and explain what causes each type. What advice for finding a job would be appropriate for someone in each type of
unemployment?
What will be an ideal response?
Frictional unemployment is the unemployment that arises from the process of matching workers with jobs. These workers are qualified; they just need to search for a job. The advice for finding a job would be to keep searching, because there are jobs available for which they are qualified.
Structural unemployment is unemployment arising from a persistent mismatch between the skills and characteristics of workers and the requirements of the jobs. The advice for finding a job would be to retrain so that they can match up with the requirements of current jobs.
Cyclical unemployment is unemployment caused by a business cycle recession. The advice for finding a job would be to hang in there and continue searching, but realize that there are less jobs available than the number of applicants. The cyclically unemployed person could perhaps get a temporary job until the economy picks up, or perhaps consider continuing his or her education while the business cycle slowdown lasts.
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 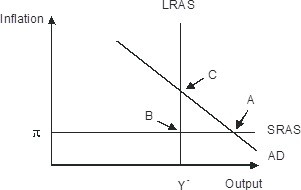
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A
In an unregulated market for healthcare, the equilibrium quantity is that at which ________ and the efficient quantity is that at which ________
A) D = S; MB = MSC B) D = S; MSB = MSC C) D = MSC; MB = MSC D) MSB = S; MB = S
If the price of milk was $1.25 a gallon and it is now $2.25 a gallon, what is the percentage change in price?
A) 4.4 percent B) 8 percent C) 44 percent D) 80 percent
If one firm in a perfectly competitive industry is somehow able to produce at a lower cost than competing firms in the short run,
a. the competing firms will adopt similar production techniques in the long run. b. the more efficient firm will earn higher profits than the competing firms in the long run. c. the competing firms will earn higher profits than the more efficient firm in the short run. d. the competing firms will go out of business in the long run.