In the condensation theory of the Moon's origin,
a. the Moon broke from a rapidly spinning Earth.
b. Earth and its Moon formed from the same cloud of matter.
c. the Moon formed elsewhere in the solar nebula and was later captured by Earth.
d. the Moon formed when a very massive planetesimal smashed into the young Earth.
b
You might also like to view...
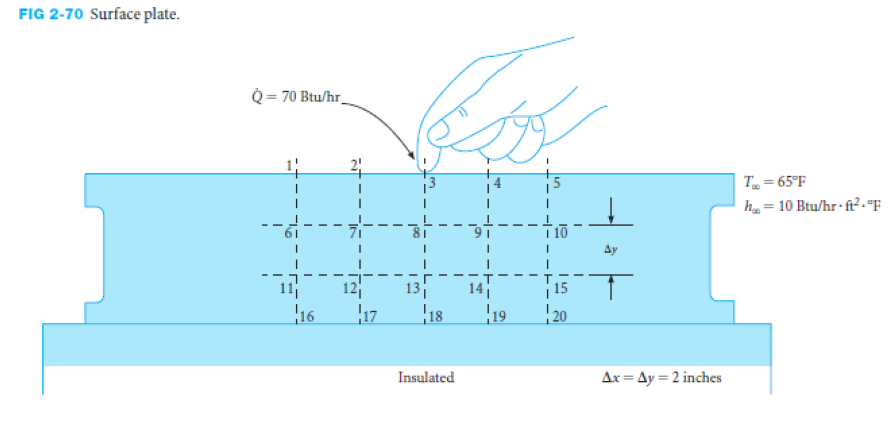
Figure 2-70 shows a section of a large surface plate used for precision measurements. A person touches the surface and thereby induces heat transfer through the plate. Neglecting radiation involved, write the node equations for nodes 1, 5, and 12.
As a huge rotating cloud of particles in space gravitate together forming an increasingly dense ball, it shrinks in size and
A) rotates slower. B) rotates at the same speed. C) rotates faster. D) cannot rotate.
A particle with a charge of 4.0 ?C has a mass of 5.0 × 10-3 kg. What electric field directed upward will exactly balance the weight of the particle?
A) 4.1 × 102 N/C B) 8.2 × 102 N/C C) 4.4 × 104 N/C D) 1.2 × 104 N/C E) 5.1 × 106 N/C
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20 rad/s. During a 5.0-s interval the angular velocity decreases to 10 rad/s. Assume that the angular acceleration is constant during the 5.0-s interval. How many radians does the wheel turn through during the 5.0-s interval?
a. 95 rad b. 85 rad c. 65 rad d. 75 rad e. 125 rad