Historically, why did the import-substitution strategy become popular among developing nations?
What will be an ideal response?
This strategy gained popularity throughout the 1950s because, at this time, most developing nations exported agricultural and mineral products-goods that often faced very unstable international market conditions. Moreover, the terms of trade for these nations seemed to be headed on a long-term decline. When a country experiences a decline in its terms of trade, its imports become relatively more expensive in its domestic market, whereas its exports become less expensive in the world market. As a result of these conditions, by the 1950s import-substitutions policies started gaining prominence.
You might also like to view...
As their relative riskiness ________, the expected return on corporate bonds ________ relative to the expected return on default-free bonds, everything else held constant
A) increases; increases B) increases; decreases C) decreases; decreases D) decreases; does not change
The monopolist faces a:
A. perfectly elastic demand curve. B. downward sloping demand curve. C. perfectly inelastic demand curve. D. perfectly elastic supply curve.
Refer to the accompanying figure. At P = 4, how does the price elasticity of demand for D1 compare to that for D2?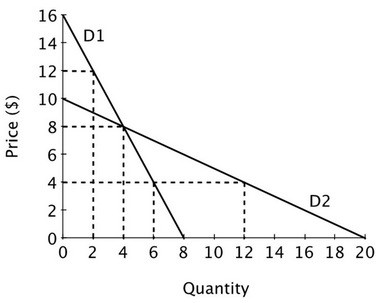
A. It will be greater for D1 than for D2. B. The price elasticity of demand for both D1 and D2 will be greater than one. C. It will be lower for D1 than D2. D. It will be equal for D1 and D2.
One way the consumer price index (CPI) differs from the GDP chain price index is that the CPI:
A. uses current year quantities of goods and services. B. includes separate market baskets of goods and services for both base and current years. C. includes only goods and services bought by typical urban consumers. D. is bias free.