While taking the NCLEX-RN, CAT examination, a graduate encounters a question about a disease process that had not been covered in any class in nursing school. Which strategy would be best for the graduate to use in answering this question?
a. Look for a totally unfamiliar answer and select it because it probably relates to the unknown disease process.
b. Select answer A and move on to the next question.
c. Try to remember a question earlier in the examination that dealt with a similar situ-ation and apply that information to the current question.
d. Select the answer that appears logical and involves general nursing care.
D
You might also like to view...
Orem says that self-care ability is affected by a number of factors, including:
a. Ethnicity, age, and gender. b. Age, gender, and developmental stage. c. Age, developmental stage, health, and environment. d. Health, environment, age, and gender.
A patient with a temporary pacemaker has this cardiac rhythm. What nursing intervention is indicated?
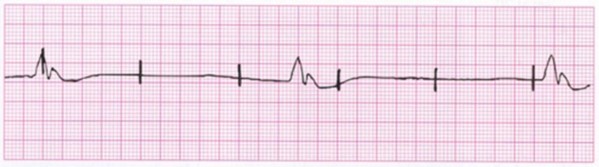
1. Turn the impulse generator off, wait 30 seconds, and turn it back on.
2. Call for a STAT portable chest x-ray.
3. Check for a damaged lead wire.
4. Decrease the pacemaker sensitivity.
To adequately prepare for the NCLEX-RN® examination, which action by the graduate nurse is advised?
a. Begin planning early at least 6 months ahead. b. Begin planning no more than 3 months ahead. c. Wait for the state board of nursing to con-tact the applicant about filing deadlines. d. Call the state board of nursing every week to set up a testing time.
A nurse is assisting with a client health history for a 5-year-old boy being admitted to the hospital for surgery. Which of the following is a recommended guideline for gaining the child's cooperation?
A) Keep assessment equipment away from the child's view so as not to scare him. B) Direct all questions to the family caregiver. C) Allow the child to sit in the caregiver's lap for as much of the interview as possible. D) Do not be afraid to restrain the child if he is not cooperating.