What do we call the monetary difference between the amount a consumer is willing and able to pay for an additional unit of a good and what the consumer actually pays?
a. deadweight loss
b. market price
c. consumer surplus
d. consumer sovereignty
c. consumer surplus
You might also like to view...
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question below.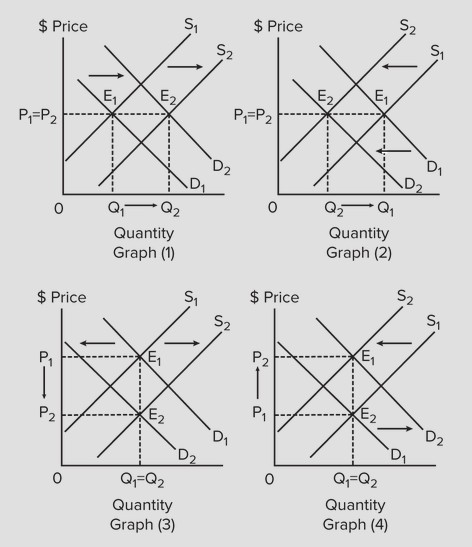 In which graph would the indicated shifts cause equilibrium quantity to definitely rise, but the effect on price is indeterminate?
In which graph would the indicated shifts cause equilibrium quantity to definitely rise, but the effect on price is indeterminate?
A. graph (1) B. graph (2) C. graph (3) D. graph (4)
Under the gold standard
A) a perpetual surplus is possible. B) a perpetual deficit is possible. C) a perpetual surplus is impossible, but a perpetual deficit is possible. D) a perpetual deficit is impossible, but a perpetual surplus is possible. E) a perpetual surplus is impossible.
The law of diminishing product states that if increasing quantities of a variable factor are applied to a given quantity of fixed factors, then:
a) the MP and the AP of the variable factor will eventually decrease. b) TP will eventually begin to fall. c) the AP will eventually decrease, but only if TP is held constant. d) the MP will eventually decrease with constant AP. e) the AP will eventually decrease with constant MP.
Capitalism gets its name from the fact that capital resources are mostly:
A. Owned by the state or government B. Given the highest priority in the economy's income distribution C. Treated as private property D. In the form of money and financial resources