Two concentric imaginary spherical surfaces of radius R and 2R respectively surround a positive point charge ?Q located at the center of the surfaces. When compared to the electric flux ?1 through the surface of radius R, the electric flux ?2 through the surface of radius 2R is
a.
![]() .
.
b.
.
c
You might also like to view...
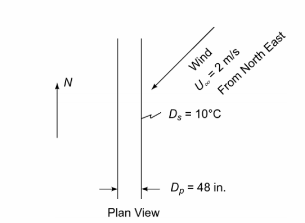
The Alaska Pipeline carries 2 million barrels of crude oil per day from Prudhoe Bay to Valdez covering a distance of 800 miles. The pipe diameter is 48 in. and it is insulated with 4 in. of fiberglass covered with steel sheeting. Approximately half of the pipeline length is above ground, running nominally in the north-south direction. The insulation maintains the outer surface of the steel sheeting at approximately 10°C. If the ambient temperature averages 0°C and prevailing winds are 2 m/s from the northeast, estimate the total rate of heat loss from the above-ground portion of the pipeline.
GIVEN
• Fiberglass insulated pipe with air flow at 45° to its axis
• Insulation is covered with sheet steel
• Length of pipe above ground (L) = (800 miles)/2 = 400 miles
• Pipe diameter (Dp) = 48 in.
• Insulation thickness (t) = 4 in.
• Sheet steel temperature (Ts) = 10°C
• Average ambient air temperature (T?) = 0°C
• Average air velocity (U?) = 2 m/s
FIND
• The total rate of heat loss from the above ground portion of the pipe (q)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Thermal resistance of the sheet steel as well as contact resistance can be neglected
SKETCH
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. A given object always has a specific moment of inertia I, independent of the axis around which it rotates (as long as the axis goes through the object’s center of mass). 2. An isolated star collapses so that its radius is half its original radius. Both its angular momentum and its rotational energy must be conserved.
An 8.0-kg object moving 4.0 m/s in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional collision with a 2.0-kg object moving 3.0 m/s in the opposite direction. The final velocity of the 8.0-kg object is 2.0 m/s in the positive x direction. What is the total kinetic energy of the two-mass system after the collision?
a. 32 J b. 52 J c. 41 J d. 25 J e. 29 J
A brass rod with a length of 10.0 cm is placed end to end with an aluminum rod with a length of 30.0 cm and this system is placed between a hot temperature of 100 and a cold temperature of 10.0
and a cold temperature of 10.0 The coefficient of thermal conductivities of the brass and the aluminum are 100 W/m C and 230 W/m
The coefficient of thermal conductivities of the brass and the aluminum are 100 W/m C and 230 W/m respectively. The rods have the same cross sectional area of 20.0 cm2. What is the heat flow from the hot temperature to the cold temperature?
respectively. The rods have the same cross sectional area of 20.0 cm2. What is the heat flow from the hot temperature to the cold temperature?
A. 55.3 W B. 65.3 W C. 70.3 W D. 78.1 W E. 85.3 W