The book cites a result where after of the implementation of the congestion tax in Stockholm, Sweden of $1.50-$3.00, traffic volume was reduced and travel time for cars and buses was cut in half. This is an example of:
A. responding to incentives.
B. the role of pricing in allocating resources.
C. caveat emptor.
D. comparative advantage.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Looking at inflation rates in the United States since the 1970s we see that
A) inflation fell the most during the 1970s productivity slowdown. B) the highest inflation rates were the double digits during the 1990s. C) the inflation rate increased with the increased growth of the 1990s. D) the 1970s experienced the highest inflation rates.
Refer to Table 4-4. The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Curly, Moe, and Larry, are willing to pay for a bottle of champagne. If the price of one of the bottles is $27 dollars, total consumer surplus will be
A) $0. B) $14. C) $26. D) $53.
Refer to the graph shown.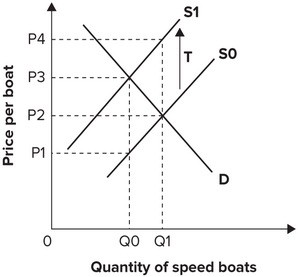 As a result of a tariff T imposed on speedboats, the price domestic consumers pay for speedboats probably will likely be:
As a result of a tariff T imposed on speedboats, the price domestic consumers pay for speedboats probably will likely be:
A. P1. B. P2. C. P3. D. P4.
The point where the central bank's target inflation rate is consistent with the long-run real interest rate lies:
A. on the monetary policy reaction curve. B. on the horizontal (inflation) axis. C. above the monetary policy reaction curve. D. below the monetary policy reaction curve.