The rigid body shown is rotated about an axis perpendicular to the paper and through the point P. If M = 0.40 kg, a = 30 cm, and b = 50 cm, how much work is required to take the body from rest to an angular speed of 5.0 rad/s? Neglect the mass of the connecting rods and treat the masses as particles.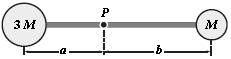
A. 2.9 J
B. 2.6 J
C. 3.1 J
D. 3.4 J
E. 1.6 J
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The spreading of different wavelengths of light due to slightly different indices of refraction is known as
A. Refraction B. Dispersion C. Immersion D. Total internal reflection
The reinforcing material with the highest strength available for composites is
(a) Whiskers (b) Graphite fibers (c) SiC fibers (d) OUHMWPE
You are holding on to one end of a long string that is fastened to a rigid steel light pole. After producing a wave pulse that was 5 mm high and 4 cm wide, you want to produce a pulse that is 4 cm wide but 7 mm high. You must move your hand up and down once,
a. the same distance up as before, but take a shorter time. b. the same distance up as before, but take a longer time. c. a smaller distance up, but take a shorter time. d. a greater distance up, but take a longer time. e. a greater distance up, but take the same time.
A child is riding a merry-go-round, which has an instantaneous angular speed of 1.25 rad/s and an angular acceleration of 0.745 rad/s2
The child is standing 4.65 m from the center of the merry-go-round. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the child? (b) What angle does the acceleration of the child make with the tangential direction?