Answer the next question based on the following demand and cost data for a specific firm.Demand DataCost Data(1) Price(2) Price(3) QuantityTotal OutputTotal Cost$50$3522$4545303355402544703520559030156611525107714520588180If columns 1 and 3 are this firm's demand schedule, then economic profit will be
A. $70.
B. $90.
C. $80.
D. $60.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 22.2 below. Suppose that the supply of land is constant at L acres, and Price per acre is $400. In addition, the before-tax demand for land can be characterized by the equation P = 500 - 2L, where L is the acres of land and P is the price.
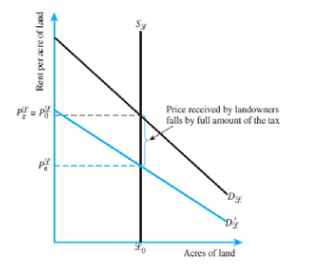
(A) What is the constant supply of land (L) in the market?
(B) If the after-tax demand curve, P , can be written as P = 400 - 4L, what is P , and how
much tax revenue is generated?
Spending VCU4 on real-world goods and services causes the nation's:
a. Monetary base to remain the same. b. M2 money supply to fall. c. M2 money multiplier to fall. d. Monetary base to rise.
Government output is hard to account for because government
A. is so large. B. provides goods that have no resale value. C. keeps secrets about what it produces. D. goods are generally not sold or produced in easily measurable units.
The price of peanuts drops from 50 cents to 25 cents per pound. How and why might an individual and a group of 1,000 people respond to this price drop very differently?
What will be an ideal response?