Suppose the cafeteria at a university puts healthy foods such as fruit and yogurt in an easily accessible location but places junk foods somewhere slightly less prominent. This would be an example of a(n):
A. nudge.
B. push.
C. irrational behavior.
D. incentive compatibility problem.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figures d and e. Water is crucial for survival, but it is particularly valuable during a drought when water is scarce. The probability of a drought is (1 - P), WD represents the quantity of water in a drought, while WR represents the quantity of water in a rainy season. Which set of indifference curves above best represent a relatively high probability of a drought?
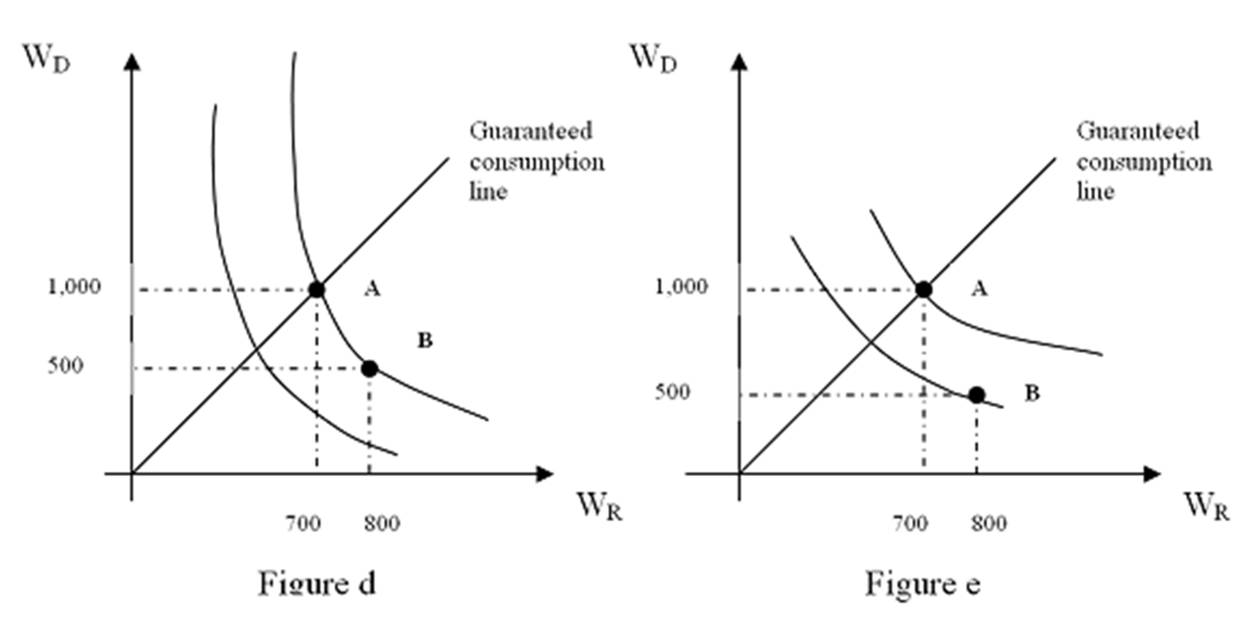
A. Figure d
B. Figure e
C. Probabilities do not influence indifference curves.
D. Both Figures represent a relatively low probability of a drought.
When the price of a good changes but the price of the only other good bought by a consumer stays constant, his
a. budget line shifts. b. indifference curves shift. c. budget line changes slope. d. indifference curves change slope.
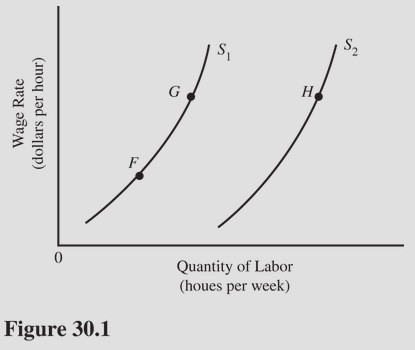 In Figure 30.1, the labor supply could shift from S1 to S2 due to all of the following except
In Figure 30.1, the labor supply could shift from S1 to S2 due to all of the following except
A. A decrease in the attraction of leisure activities. B. An increase in the number of workers willing to work in this labor market. C. Fewer workers preferring to work in this labor market. D. A decrease in the payroll tax on workers.
When you use money to purchase groceries, money is functioning as a store of value.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)