Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD1. This is an example of
A) laissez-faire.
B) partial crowding-out effect.
C) the free rider problem.
D) complete crowding-out effect.
D
You might also like to view...
A decrease in demand would be represented by
A) the price of a good going from $3 to $4. B) an increase in the cost of resources used to produce the good. C) a movement along the demand curve. D) a shift of the demand curve to the left.
If an excise tax is imposed on steak,
a. the government's tax revenue will decrease b. the government's tax revenue will increase c. the amount of steak produced and sold will increase d. the market price of steak will decrease e. the market price will rise but the market quantity will be unaffected
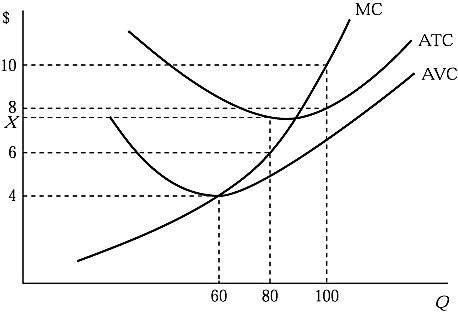
 Figure 6.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose that market price falls to $6. If the firm produces at an output level that causes it to suffer an economic loss of $120, its average total cost (X) is:
Figure 6.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose that market price falls to $6. If the firm produces at an output level that causes it to suffer an economic loss of $120, its average total cost (X) is:
A. $8. B. $7.50. C. $6.50. D. $4.
Production refers to
A) physically producing material goods only. B) any activity of a firm, whether a corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. C) any activity that results in the conversion of resources into goods or services that can be consumed. D) any activity that causes a material conversion of manufactured goods.