Most government purchases are made at the federal level and not at the state level
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
False
You might also like to view...
Arnold Marion, a first-year economics student at Fazer College, was given an assignment to find an example of price discrimination and present it to his class
When asked for his example Arnold said "I went to a Milwaukee Brewers baseball game with my cousin last week. We paid $25 each for our seats in left field. My aunt and uncle paid $50 each for their tickets; they sat five rows behind the first base dugout. This is an example of price discrimination since we paid different prices for the same product, and the differences were not due to differences in costs." How would Arnold's economics instructor assess Arnold's example? A) He would agree with Arnold that he had found an example of price discrimination, but would add that arbitrage would occur if ticket scalpers sold Brewers tickets for more than the prices Arnold and his uncle paid. B) He would agree with Arnold that he had found an example of price discrimination and would explain that the elasticity of demand for Brewers tickets is different for Arnold and his uncle. C) He would disagree with Arnold's example because there were differences in transactions costs for the $50 tickets and the $25 tickets. D) He would disagree with Arnold's example because the $25 seats and the $50 seats were not the same products.
Refer to the table below. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.00 per unit, what is the profit-maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 1?
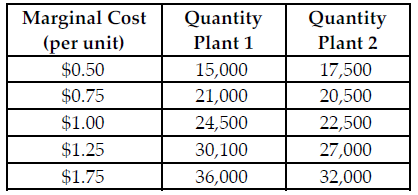
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi-plant firm with two production facilities. The above table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
A) 24,500
B) 27,000
C) 32,000
D) 22,500
Which among the following does not determine the shape of the demand curve for a good under different market structures?
a. Number of substitutes in the market b. Importance of the good in a consumer's budget c. Cost structure of the firm d. Price-elasticity of demand e. The length of time being considered
Normative analysis:
A. aims at determining only the economic consequences of a particular policy. B. does not depend on the analyst's values. C. focuses on the actual effects of a policy. D. addresses the question of whether a policy should be used.