Expected value is
a. (Probability of state A+Value in state A) (Probability of state B+Value in state B)
b. (Probability of state AValue in state A)+(Probability of state BValue in state B)
c. (Probability of state AValue in state A)-(Probability of state BValue in state B)
d. (Probability of state A-Value in state A) (Probability of state B-Value in state B)
C
You might also like to view...
In the figure above, the length of the double sided arrow is the
A) consumer surplus. B) deadweight loss. C) producer surplus. D) economic loss per unit. E) economic profit.
Over the last ten years productivity grew more slowly in Iberia than in Aire while the population and total hours worked remained the same in both countries. It follows that
a. real GDP per person must be lower in Iberia than in Aire. b. real GDP per person grew more slowly in Iberia than in Aire. c. the standard of living must be higher in Iberia than in Aire. d. All of the above are correct.
Suppose two types of consumers buy suits. Consumers of type A will pay $100 for a coat and $50 for pants. Consumers of type B will pay $75 for a coat and $75 for pants. The firm selling suits faces no competition and has a marginal cost of zero. The optimal commodity bundling strategy is:
A. Charge $100 for a suit. B. Charge $125 for a suit. C. Charge $75 for a suit. D. Charge $150 for a suit.
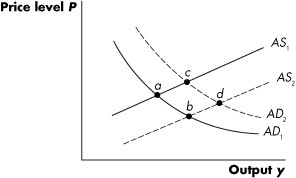
 Refer to Figure 14.2. A movement from point c to point b could be caused by a simultaneous ________ and ________.
Refer to Figure 14.2. A movement from point c to point b could be caused by a simultaneous ________ and ________.
A. decrease in government spending; decrease in the price of oil B. decrease in taxes; increase in the price of oil C. increase in taxes; decrease in government spending D. increase in government spending; increase in the money supply