Suppose that the government decided to increase interest rates in order to encourage saving. Would this likely lead to an increase in investment and higher future economic growth rates? Explain
No. The increase in interest rates might encourage more saving (less present consumption) but not more investment. The opportunity cost of the funds would rise, and make it more difficult to pay back borrowed money than if interest rates were lower. Most likely, investment would decrease instead of increase.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following are lags that fiscal policy makers must cope with?
A) effect time lags B) recognition time lags C) action time lags D) All of the above are correct.
If there are a large number of firms in a monopolistically competitive industry
A) long-run profit will be equal to zero. B) the country in which the firms are located can be expected to export the goods they produce. C) there will be barriers to entry that prevent addition firms from entering the industry. D) the firms will converge production on a standardized product. E) there will be a small number of firms that are very large and the rest will be very small.
Food stamps and Medicaid are in-kind transfer programs
a. True b. False
Refer to the figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and S t is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. The total tax collection from this excise tax will be area:
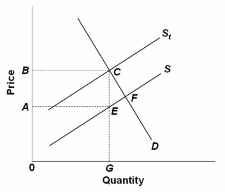
A. ABCE + ECF.
B. ABCE.
C. ECF.
D. 0BCG.