There are ten states in the democratic nation of Katlandia, and each state has ten thousand residents. Although incomes vary, each Katlandian pays a tax equal to the total cost of all government projects divided by the number of residents in the country. Currently, two states each have one army base. An army base adds $2 million to a state's local economy each year. In addition, in terms of increased security, the annual marginal benefit to Katlandia of having an additional army base is shown below. The total cost of an army base is $8 million per year.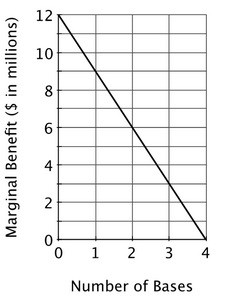 It is socially optimal for Katlandia to have:
It is socially optimal for Katlandia to have:
A. four army bases.
B. two army bases.
C. three army bases.
D. one army base.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A second-price auction
a. is also called an English auction b. is where the highest bidder wins and pays the amount of the next highest bid c. is where the sole remaining bidder wins and pays his winning bid d. all of the above
Which of the following will most likely cause movement along the consumption function?
a. a change in disposable income b. a change in interest rates c. a change in tastes d. a change in consumers' expectations
Assume that the central bank lowers the discount to increase the nation's monetary base. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real exchange rate and monetary base in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic system returns to complete equilibrium. Assume the nominal exchange rate
is stated as: (Domestic currency per foreign currency). a. The real exchange rate rises and monetary base rises. b. The real exchange rate rises and monetary base falls. c. The real exchange rate and monetary base fall. d. The real exchange rate and monetary base remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
As you move down the production possibility frontier, the absolute value of the marginal rate of transformation
A. increases. B. initially decreases, then increases. C. decreases. D. initially increases, then decreases.