The strong appreciation of the dollar for the last part of the 1990s:
A. played a key role in keeping inflation in check even though the economy was growing rapidly.
B. was a benefit to all U.S. residents but costly to most foreign producers.
C. was a benefit to U.S. exporters, but put a severe strain on U.S. Importers.
D. was welcomed by all U.S. manufacturers.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. Recall that the bidders only know their own private value of the item and they do not know the other participants' private values. Further, assume each participant will submit bids using their optimal strategy. If the participants are bidding in a Dutch auction, Bidder ________ wins the auction and pays ________.
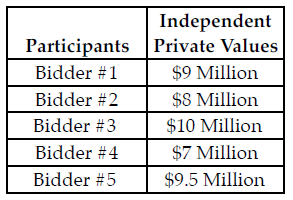
The table above lists the independent private values of five participants in an auction. Each of the bidders only knows their own value and does not know the private values of the other participants.
A) #3; a value less than $10 million and greater than $9.5 million
B) #5; a value less than $10 million and greater than $9.5 million
C) #5; 9.5 million
D) #3; $10 million
A perfectly competitive employer of an input will maximize profits from the employment of the input by equating:
a. the value of the marginal product of the input with the price of the output. b. the marginal product of the last unit of the input employed with the input price. c. the input price with the price of the product produced. d. the marginal revenue product of the input with the input price. e. the marginal product of the last unit of the input employed with the price of the product produced.
Using the output at which the aggregate expenditure curve intersects the 45-degree line, we can identify
A. A consumption shortfall at the intersection point. B. Full employment to the left of the intersection point if there is a recessionary gap. C. Equilibrium (macro) at the intersection point. D. Dissaving to the right of the intersection point.
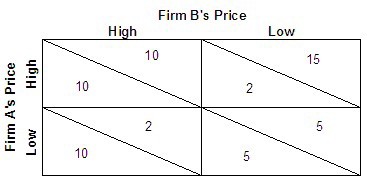 Refer to the above payoff matrix for the profits (in $ millions) of two firms (A and B) and two pricing strategies (high and low). Which of the following is the outcome of the dominant strategy without cooperation?
Refer to the above payoff matrix for the profits (in $ millions) of two firms (A and B) and two pricing strategies (high and low). Which of the following is the outcome of the dominant strategy without cooperation?
A. Both firm A and firm B choose the low price. B. Firm A chooses the high price while firm B chooses the low price. C. Both firm A and firm B choose the high price. D. Firm A chooses the low price while firm B chooses the high price.