Suppose that there are diminishing returns to capital. Suppose also that two countries are the same except one has less capital and so less real GDP per person. Suppose that both increase their saving rate from 3 percent to 4 percent. In the long run
a. both countries will have permanently higher growth rates of real GDP per person, and the growth rate will be higher in the country with more capital.
b. both countries will have permanently higher growth rates of real GDP per person, and the growth rate will be higher in the country with less capital.
c. both countries will have higher levels of real GDP per person, and the temporary increase in growth in the level of real GDP per person will have been greater in the country with more capital.
d. both countries will have higher levels of real GDP per person, and the temporary increase in growth in the level of real GDP per person will have been greater in the country with less capital.
d
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 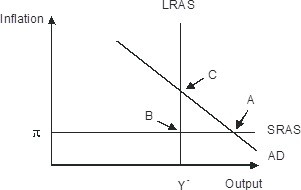
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Economic depreciation is
A. the change in the distribution of real income induced by a tax. B. the extent to which an asset decreases in value during a period of time. C. the money value of the net increase in an individual's power to consume during a period. D. a subtraction from tax liability (as opposed to a subtraction from taxable income).
A price floor in the cotton market will result in an excess supply unless
a. the excess demand for cotton is reduced to zero b. it is immediately followed by a shift to the right in the demand curve that reduces the excess supply to zero c. the excess supply of cotton is equal to the excess demand for cotton at the floor price d. the supply is immediately stimulated to reduce the excess demand that results from the excess supply e. the quantity demanded shifts to the right
If quantity demanded decreased by 3 units at each price, you would conclude that
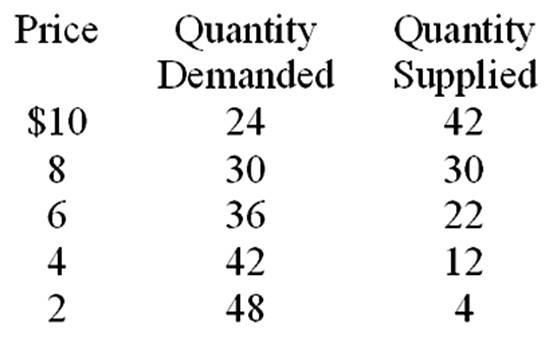
A. demand increased.
B. demand decreased.
C. supply increased.
D. supply decreased.