In the small town of Springfield, Duffman observes that the price of beer has fallen. Duffman concludes that the total amount of money spent buying beer has to fall since the price of beer is lower now. Is he correct? Why or why not? Clearly explain your answer.
What will be an ideal response?
Duffman is incorrect in arguing that a lower cost of beer has to reduce the total amount of money spent on buying beer. Total spending on beer (total revenue to the industry) is the product of price and quantity. A lower price of beer certainly reduces per-unit revenue, but the law of demand implies more people will drink beer at the lower price. So the quantity of beer demanded increases. It is uncertain whether total spending on beer will increase or decrease: It depends on the elasticity of demand for beer. If the demand for beer is inelastic, then total spending would drop. But if the demand for beer is elastic, then total spending on beer would increase at the lower price, as the quantity sold would have increased substantially.
You might also like to view...
In the one-period competitive model we have been studying
A) both consumption and total factor productivity are exogenous. B) consumption is exogenous and total factor productivity is endogenous. C) consumption is endogenous and total factor productivity is exogenous. D) both consumption and total factor productivity are endogenous.
One major part of the opportunity costs of one's decision to go to college after high-school graduation is the:
A. Additional income that one can get if one had a college degree B. Education that one gets while in college C. High-school diploma needed in order to apply for college D. Full-time job that one could have gotten instead of going to college
The resource income earned by those who supply labor services is called
A) wages and salaries. B) stock options. C) profit. D) bonus.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 4.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.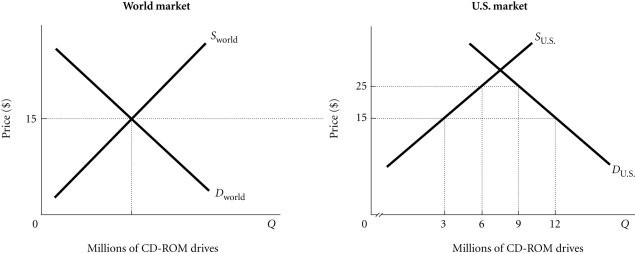 Figure 4.5Refer to Figure 4.5. Assume that initially there is free trade. If the United States then imposes a $10.00 tariff per CD-Rom drive on imported CD-Rom drives,
Figure 4.5Refer to Figure 4.5. Assume that initially there is free trade. If the United States then imposes a $10.00 tariff per CD-Rom drive on imported CD-Rom drives,
A. the quantity of CD-Rom drives supplied by U.S. firms will increase by 3 million. B. U.S. imports of CD-Rom drives will increase by 3 million. C. the quantity of CD-Rom drives demanded will be reduced by 6 million. D. the price of CD-Rom drives in the United States will decrease to $5.