When a firms "dumps" some of its products in another country, it
A) creates an environmental hazard in the receiving country.
B) sells its goods abroad at a price lower than it costs to produce the goods.
C) increases the total level of employment in the receiving country.
D) is specializing according to comparative advantage.
B
You might also like to view...
Need-based spending ________ during an expansion and ________ during a recession, which leads to larger budget deficits during the ________ phase of the business cycle
A) increases; decreases; recession B) decreases; increases; expansion C) decreases; increases; recession D) decreases; decreases; expansion E) increases; decreases; expansion
Assume the technology for producing personal computers improves and, at the same time, individuals discover new uses for personal computers so that there is greater utilization of personal computers. Which of the following will happen to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity?
A) Price will increase; quantity cannot be determined. B) Price will decrease; quantity cannot be determined. C) Quantity will increase; price cannot be determined. D) Quantity will decrease; price cannot be determined.
Assume you are holding Treasury securities and have sold futures to hedge against interest-rate risk. If interest rates rise
A) the increase in the value of the securities equals the decrease in the value of the futures contracts. B) the decrease in the value of the securities equals the increase in the value of the futures contracts. C) both the securities and the futures contracts decrease in value. D) both the securities and the futures contracts increase in value.
With reference to the graph above, if the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6 was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then normative analysis would conclude that:
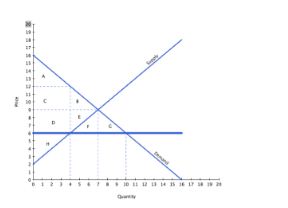
A. the policy was effective, since surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
B. the policy was ineffective, since surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
C. the policy was effective, since surplus lost by producers through lower prices is less than the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices.
D. there is no "right" conclusion to be reached (in a normative sense), since people have different opinions concerning what constitutes a better outcome.