Which of the following is the most common type of main-sequence star?
A) an O star
B) an A star
C) an F star
D) an M star
E) a G star
D) an M star
You might also like to view...
What is the primary reason we divide the ingredients of the solar nebula into four categories (hydrogen/helium gas; hydrogen compound; rock; metal)?
a. The amount of energy required to ionize these materials varies considerably. b. The temperature at which these materials condense into a solid varies considerably. c. The atomic mass number of these materials differs considerably. d. The abundance of these materials depended on their location in the solar nebula.
The following statements are all true. Which one counts as an "exception to the rule" in being unusual for our solar system?
A) Venus does not have a moon. B) Jupiter has a very small axis tilt. C) Saturn has no solid surface. D) The diameter of Earth's Moon is about 1/4 that of Earth.
Which of the following is an example of a star?
A) Venus B) Pluto C) The Sun D) The Moon
If the resultant force acting on a 2.0-kg object is equal to 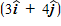
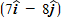
src="https://sciemce.com/media/2/ppg__cognero__Chapter_9_Energy_in_Nonisolated_Systems.__media__e45505c6-cd94-4a7d-9369-dadf59e7a269.PNG" data-wiris-created="true" class="Wirisformula" align="middle" />m? A. +36 J B. +28 J C. +32 J D. +24 J E. +60 J