The term "free rider"
a. refers to the reduction of incentives for an individual to provide effort.
b. describes the privatization of goods and property.
c. refers to a situation in which resources are overused and quickly exhausted.
d. describes people who did not pay for their ship travel to the colonial US because their relatives would pay their fares once they arrived.
a. Refers to the reduction of incentives for an individual to provide effort.
You might also like to view...
What famous economist said that the market economy seemed to be controlled by an invisible hand?
a. Alfred Marshall. b. Adam Smith. c. Karl Marx. d. Robert L. Heilbroner.
The production possibilities frontier rotates outward along one of the axes when:
a. there is a technological change that enhances the production of both goods. b. there is a decrease in the availability of resources used to produce both goods. c. there is a decrease in the quality of resources used to produce both goods. d. there is a technological change that enhances the production of only one of the goods.
A World View article, "The Female 'Inequality Trap,'" says that in many poor nations the "… returns on female human capital investment is low." When women are not allowed to work outside the home or to receive an education, this is referred to as
A. An inequality trap. B. A justice gap. C. A productivity trap. D. A prejudice gap.
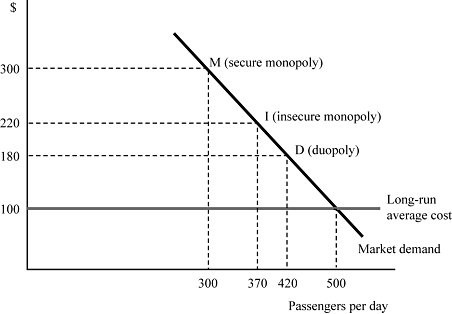
 In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is 130 passengers per day, what price should Smart Fly charge to secure the entry-deterring quantity?
In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is 130 passengers per day, what price should Smart Fly charge to secure the entry-deterring quantity?
A. $300 B. $220 C. $180 D. $100