The Reynolds number Re is a dimensionless group that characterizes the intensity of a flow. For large Re, a flow is turbulent; for small Re, it is laminar. For pipe flow, Re ?u?D/?, where D is pipe diameter and ? is dynamic viscosity.
(a) If D and ? are fixed, what is the effect of increasing mass flow rate ? on Re?
(b) If ? and ? are fixed, what is the effect of increasing D on Re?
The mass flowrate, ?, is related to the density, diameter, and average velocity by
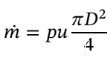
Thus,
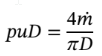
And
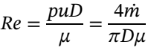
Thus, the Reynolds number is directly proportional to the mass flow rate.
a. The expression in part (a) shows that in this case the Reynolds number is inversely proportional to the diameter, D.
You might also like to view...
How is mechanical interlocking accomplished?
What will be an ideal response?
Hybrid electric vehicles usually require special engine oil of what viscosity?
A) SAE 10W-30 B) SAE 5W-30 C) SAE 5W-40 D) SAE 0W-20
What are notes and leaders used for?
What will be an ideal response?
This type of diagram provides the technician with the unit's sequence of operations
A) Ladder B) Point-to-point C) Pictorial D) Schematic